Introduction
Industries generate a substantial volume of wastewater, posing a serious environmental threat. An effective effluent treatment plant (ETP) is crucial for safely disposing of this wastewater, as it plays a pivotal role in reducing pollution levels. Without the implementation of proper treatment processes, industrial waste can infiltrate nearby water bodies, leading to contamination that jeopardizes aquatic ecosystems and endangers public health.
ETPs help protect the environment and safeguard communities from the harmful effects of industrial discharges by ensuring that wastewater is treated efficiently.
What Is an Effluent Treatment Plant?
An effluent treatment plant is a system designed to treat industrial wastewater. It removes harmful chemicals, toxins, and pollutants before releasing the water into the environment. Various treatment processes, including physical, chemical, and biological, ensure water meets safety standards.
Key Benefits of an Efficient ETP
Environmental Protection
Industries discharge hazardous waste that can damage aquatic ecosystems. An effective ETP minimizes pollution, preserves biodiversity, and maintains water quality.
Regulatory Compliance
Governments enforce strict wastewater treatment regulations. Industries that fail to comply face heavy fines and legal action. A well-maintained ETP helps businesses adhere to environmental laws.
Cost Efficiency
Recycling and reusing treated water reduce operational costs. Industries can lower water bills and minimize expenses on freshwater procurement.
Improved Public Health
Untreated wastewater can contaminate drinking water sources, leading to diseases. Proper treatment prevents health hazards, ensuring safer communities.
Sustainable Industrial Growth
Eco-friendly practices enhance a company’s reputation. Implementing an efficient ETP supports corporate social responsibility and promotes sustainability.
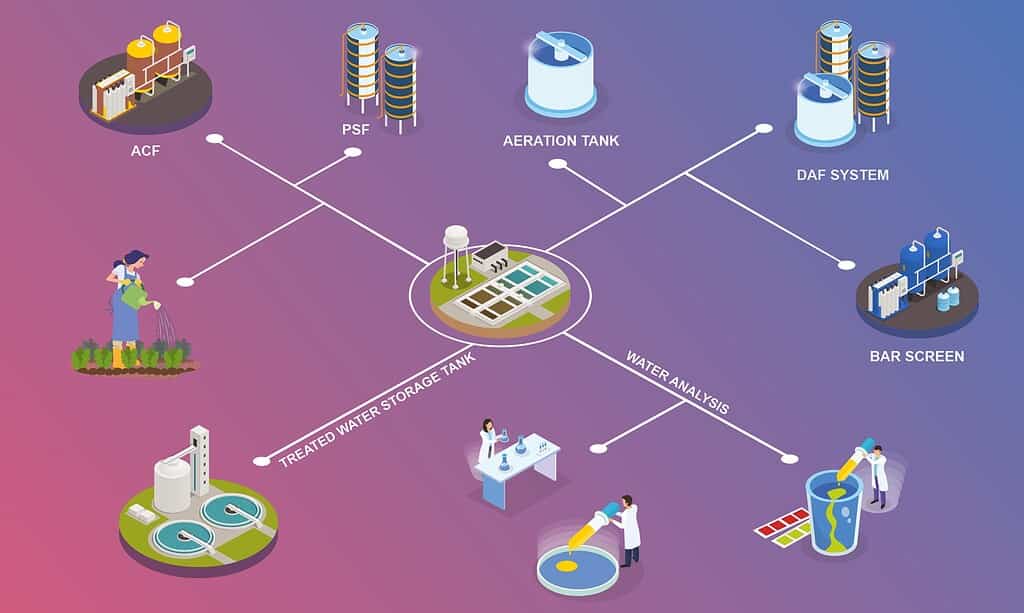
How Does an ETP Work?
Primary Treatment
- Removes large solids and debris.
- Uses sedimentation and screening to separate pollutants.
Secondary Treatment
- Biological processes break down organic matter.
- Microorganisms digest harmful substances, reducing toxicity.
Tertiary Treatment
- Advanced filtration removes residual contaminants.
- Chemical treatments neutralize hazardous compounds.
Sludge Management
- Treats solid waste generated during purification.
- Converts sludge into reusable resources or safely disposes of it.
Industries That Need ETPs
Textile Industry
- Produces dyes and chemicals that pollute water sources.
- ETPs remove toxic residues before disposal.
Pharmaceutical Industry
- Generates hazardous chemical waste.
- Proper treatment prevents contamination of water bodies.
Food and Beverage Industry
- Discharges organic waste and oils.
- ETPs ensure hygiene and safety in wastewater disposal.
Chemical Manufacturing
- Produces toxic effluents that require advanced treatment.
- Reduces environmental risks and regulatory violations.
Conclusion
A well-designed and efficient effluent treatment plant is essential for every industrial operation. It plays a crucial role in safeguarding the environment by minimizing pollution and protecting water quality. Moreover, it ensures compliance with stringent regulatory requirements, helping businesses avoid costly fines and legal issues.
By investing in advanced wastewater treatment technologies, companies promote sustainability and improve their public image and brand reputation. Emphasizing eco-friendly solutions is vital for fostering long-term growth and ensuring the safety of our natural resources, ultimately contributing to a healthier planet for future generations. Industries must prioritize these sustainable practices to thrive in an increasingly eco-conscious market.